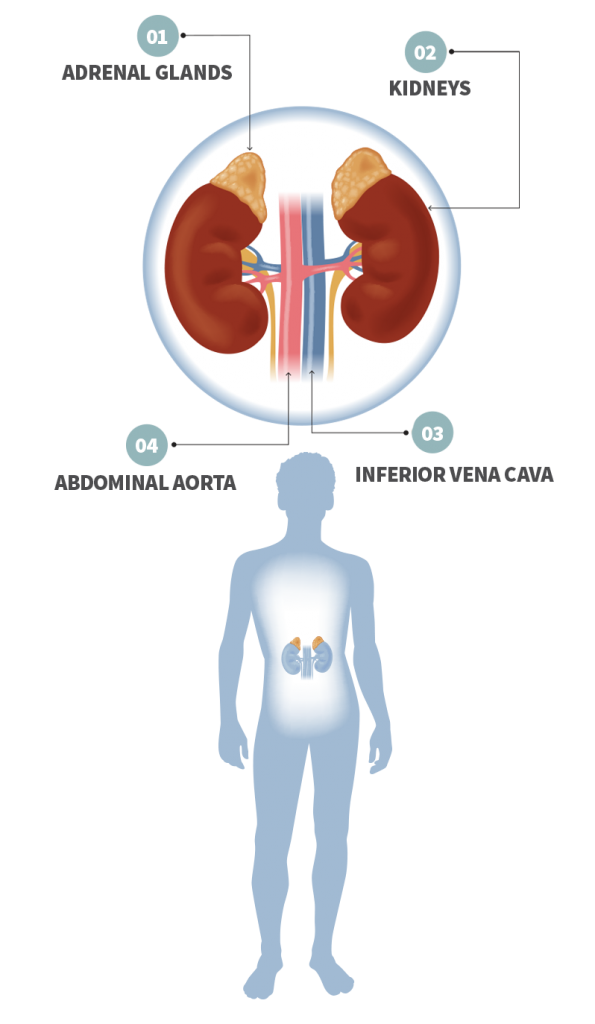
The adrenal glands are typically found just above the kidneys and play important roles in making hormones that help control blood pressure, help the body respond to stress and illness, and help with sexual vitality. The adrenal glands can fail due to a number of causes or develop tumors that may secrete excessive amounts of hormones. In addition, such tumors may be benign or malignant.
Evaluation of adrenal function includes a careful history for suggestive symptoms and blood tests including levels of hormones made by the adrenal glands. Imaging by CT and/or MRI scanning can also be helpful in making a proper diagnosis and is typically required for planning an optimal treatment.
Adrenal insufficiency can be due to failure of the glands themselves (“primary” AI) or failure of the pituitary gland to stimulate the adrenal glands (“secondary” AI). Symptoms commonly include weight loss, fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, dizziness and dehydration.
Primary AI is due to destruction of the outer part of the adrenal gland, called the cortex. This is most commonly due to an autoimmune disease called Addison’s disease, caused by an immune response against the adrenal cortex.
Secondary AI is sometimes caused by the use of excessive steroid medications such as prednisone.